Read more
To this end, Eurobank has designed, approved and is currently implementing its Sustainability Strategy, which addresses its financing and products, operational activities and footprint. Through a set of actions with measurable targets, the Sustainability Strategy outlines the Group's vision in the short, medium and long term, focusing on environmental impact, its social footprint, and the sustainability impact on the market and its portfolio.
The Sustainability Strategy includes targets and commitments along 2 key pillars:
the Operational Impact Strategy (OIS) and the Financed Impact Strategy (FIS).
| Sustainability Strategy | |
|---|---|
| Operational impact strategy | Financed impact strategy |
|
|
Operational impact strategy, commitments and targets
The Bank’s operational impact strategy is based on 3 pillars, each of which is supported by specific objectives, commitments and targets.
| Commitments and targets | ||
|---|---|---|
| Environmental impact |
Societal impact | Governance and Business impact |
|
1. Achieve net zero by 2033 for scope 1 & 2 and by 2050 for scope 3 emissions
|
5. Embed a diverse and inclusive internal environment by 2030
|
10. Intensify sustainability in procurement practices by 2024
|
|
2. Accelerate transition towards a paperless banking network by 2028
|
6. Encompass a wellbeing culture by 2026
|
11. Extend internal ESG engagement by 2025
|
|
3. Extend circular economy practices by 2025
|
7. Stimulate innovative, inclusive and youth-focused entrepreneurship by 2025
|
12. Boost internal ESG awareness by 2025
|
|
4. Accelerate preservation of natural resources – water by 2026
|
8. Rationalise Socio-Economic Impact by 2028
|
13. Boost external ESG awareness by 2025
|
|
9. Boost accessibility and inclusion for customers by 2025
|
14. Intensify ethics and transparency by 2025
|
|
For further information on the commitments and targets for the environmental impact, refer to the Sustainability Statement.
For further information on the commitments and targets for the societal impact, refer to the Sustainability Statement.
Progress on operational impact against targets for 2024
The Group is committed to specific operational impact targets, including both quantitative and qualitative elements. The Bank’s indicative achievements for 2024, the third year of OIS implementation, are presented in the following table:
| Environmental impact | Societal impact | Governance and Business impact |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Financed impact strategy, commitments and targets
The Bank recognises that sustainable development is key to prosperity. Central to its FIS is the commitment to support the transition to a greener economy by offering financing solutions that promote growth and sustainable development. As a signatory to the Principles for Responsible Banking (PRB), the Bank has been developing targets to mitigate negative impacts and amplify positive outcomes from its financing activities.
The Bank leverages tools and enablers, such as climate risk assessment exercises and the Sustainable Finance Framework, to support climate and environmental objectives. This includes providing financing, advisory and capital-raising solutions to both current and potential clients.
To better implement and monitor these objectives, the Bank is setting and refining targets, establishing comprehensive management mechanisms, KPIs and milestones. Aligning its activities with the Paris Agreement on climate change, the EU Sustainable Finance Action Plan and the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is a key aspect of this process.
The FIS focuses on fostering favourable economic, social and environmental outcomes across all aspects of its financing activities, supporting Eurobank's commitment to sustainable financing and ensuring that the Group’s financial activities align with sustainability goals. To this end, the Financed Impact Strategy is structured around the following 4 strategic pillars:
| Client Engagement and Awareness | Supporting Clients in Transition | Enablers and Tools for Sustainable Financing | Assessment and Management of sustainability-related Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Helping clients transition to more sustainable business models by raising awareness of climate change challenges and opportunities. | Facilitating the transition of clients towards sustainable practices by offering eligible financing solutions under the bank’s SFF society. |
Providing frameworks, tools, and products to underpin sustainable financing. |
Identifying and managing the sustainability-related risks within its loan and investment portfolios, including assessing exposure to transition and physical risks linked to climate change. |
| The Bank’s key enablers to advance decarbonisation | |
|---|---|
| Sector targets | Initiated the first wave of sector targets covering the Bank’s lending portfolios process in 2024, including phased target -setting up to 2050. |
| Transition pathways | Introduced transition pathways on corporate clients to achieve climate targets for the Bank’s portfolio. |
| Focused Climate Risk Assessment | Conducted focused Client Climate Risk Assessment, supplemented by climate transition scenario analysis, to support the effective implementation of its Net Zero Strategy. |
| Enhanced Risk Management Framework | Launched enhanced Risk Management Framework, with the introduction of additional Risk Appetite Statements related to Sustainability / CR&E risks. |
| Pricing approach | Adopted a pricing approach in relation to sustainable financing for the loan portfolio. |
| Sustainability/CR&E risks Datamart | Prepared for a dedicated Sustainability / CR&E risks Datamart analysis and framework. |
The Bank has set the following targets for sustainable finance disbursements in the following years:
| Targets | Portfolio Segment | Status | As of 31.12.2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Portfolio targets | Direct €2 billion in new green disbursements to corporates by 2025 (for 2023-2025) |
Corporate Banking |
On track |
c. €2 bn |
| Classify 20% of the annual new Corporate & Investment Banking (CIB) portfolio disbursements as sustainable | Corporate Banking |
Achieved |
21% |
|
| Earmark 20% stock of green exposures by 2027 for the Corporate portfolio |
Corporate Banking | On track | 16% |
|
| Mobilise €2.25 billion total green RRF funds in the Greek economy by 2026* | Corporate Banking |
On track |
€2.1 bn |
|
| €150 million new Retail green disbursements by 2026. |
Retail Banking | New target | ||
| Sectoral targets |
Direct 35% of new disbursements in the energy sector to Renewable Energy Source (RES) financing | Corporate Banking |
Achieved | 62% |
| Allocate 80% of disbursements (CIB portfolio) related to the construction of new buildings (CRE) with EPC A and above |
Corporate Banking |
Achieved | 100% | |
| Allocate 20% of new disbursements related to mortgage loans (excluding "My Home") with EPC B+ and above |
Retail Banking | New target | ||
| Other targets | Make no new investments in fixed income securities (excluding exposures in sustainability / green bonds) towards the top 20 most carbon-intensive corporates worldwide | Corporate Banking | Achieved | €0 |
| €200 million annual disbursements of Sustainability-Linked Loans for the CIB portfolio* |
Corporate Banking | On track | €707 mn | |
*The target “Double annual disbursements of sustainability-linked loans” was achieved as of 31/12/2024. The target has since been updated in 2025.
Progress on financed impact against targets for 2024
Examples of key 2024 achievements include:
- Implemented the Group’s Sustainability Strategy for 2024, including new green targets as part of its FIS.
- Rolled out the ESG Risk Assessment process for corporate clients, leveraging on the Interbank ESG Questionnaires Materiality Assessment.
- Incorporated biodiversity loss as a priority theme.
- Enhanced its monitoring framework with the adoption of additional KRIs in relation to climate risk and other environmental risks.
- Updated its Pricing Strategy by providing incentives to Corporate and Retail clients, supporting their transition journey.
- Successfully issued inaugural Green Senior Preferred Notes amounting to €850 million, marking a significant step towards sustainability goals and Net-Zero emissions by 2050.
- Provided funding in the energy sector for RES projects with an installed capacity of 6.3 GW.
- Successfully managed multiple sustainable transactions throughout 2024 (indicative green deals) by:
- Financing the largest-ever energy transaction (€3.2 billion) marked in the Athens Stock Exchange.
- Financing one of the largest solar projects (560MW) in Europe.
- Financing an investment plan towards green transition, focusing on hydrogen value chain.
- Financing the construction of 4 solar photovoltaic (PV) projects (730 MW) in Western Macedonia.
- Acting as Joint Bookrunner for the successful issuance of €750 million Senior Unsecured Green Notes.
- Introduced a comprehensive suite of financing options for small businesses and households.
- Disclosed its GHG financed emissions for loan, bond and share positions, based on the Partnership for Carbon Accounting Financials (PCAF) methodology.
- Incorporated climate risk aspects in collateral valuation.
Climate and environmental risk scenario analysis
As the global financial sector is increasingly recognising the importance of understanding and managing CR&E risks, scenario analysis has emerged as a valuable tool for assessing the potential impacts of climate change on financial institutions. Eurobank aims to provide an in-depth analysis regarding climate change transition and physical risks, so as to evaluate its resilience and adaptability to climate change. This methodological approach measures impacts based on different scenarios and time horizons (2030, 2040 and 2050), despite the uncertainty surrounding the timing and magnitude of climate change.
The analysis aims to enhance the Bank’s understanding of CR&E risks, inform strategic decision-making, and facilitate the integration of climate considerations into its risk management framework. It also aims to communicate the Bank’s approach on identifying vulnerabilities, seizing opportunities and aligning business strategies within the context of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations.
The Bank’s strategy remains adaptive, as evidenced by the scenario analysis that compares financial evolutions across sectors and geographies over various scenarios and time horizons.
The Bank uses 4 representative scenarios from the Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS) to analyse CR&E risks to the economy and financial system and assesses the physical impacts on its strategy, using 2 RCP scenarios: RCP2.6 and RCP8.5.
| NGFS scenarios | Representative Concentration Pathways (RCPs) climate scenarios |
|---|---|
| 1. Orderly: Net Zero 2050, whereby climate policies involve early, ambitious action and the impacts are low for both physical and transition risks. | 1. RCP 2.6, which incorporates strong climate policies and limits the increase in average global temperature to below 2°C. |
| 2. Disorderly: Delayed Transition, whereby climate policies are not introduced until 2030 and the outcome has a higher impact on transition risk. | |
| 3. Hot house world: Current Policies, with limited climate policies and severe physical risks and irreversible changes, including higher sea level. |
2. RCP 8.5, implying strong climate changes and the necessity of strong adaptation to the new conditions. |
| 4. Too little, too late: Fragmented World, whereby delayed and divergent climate policy ambition globally leads to elevated transition risks due to the overall ineffectiveness of the transition. |
Sustainability governance and operating model
Sustainability at Eurobank is anchored in a comprehensive Sustainability Governance structure that integrates both regulatory obligations and voluntary commitments. The Group has further enhanced its governance model by refining roles and responsibilities related to sustainability, climate, and environmental risks, embedding evolving regulatory guidelines and aligning with leading market standards.Sustainability governance
Eurobank's Sustainability Strategy integrates both regulatory and voluntary sustainability commitments, with the Board maintaining oversight through dedicated sustainability agenda items. The Group has updated its Governance structure to define roles related to sustainability, climate and environmental risks according to regulatory guidelines and industry best practices.
Using the Three Lines of Defence (3LoD) model, the Group clarifies responsibilities for managing climate-related, environmental and sustainability risks. This model enhances risk management and control within the organisation.
Recent updates to the Sustainability Governance structure aim to improve oversight of sustainability matters at Management/Board level, with direct reporting lines detailed below. Eurobank has strengthened its Sustainability Governance model to support the integration of its Sustainability Strategy and sustainability risks.

*primary reporting Line to Group Chief Risk Officer.
Enhanced Governance Structure and Committees:
- Oversight of sustainability risks at management body level through allocation of responsibilities to Board and management committees.
- Appointment of an executive member by the Board, who is responsible for climate-related and environmental risks. This member updates the Board Risk Committees (BRC) at least semi-annually.
- Establishment of 2 Committees that supplement the governance arrangements on sustainability risk, i.e. Sustainability Management Committee and Climate Risk Stress Test Committee.
- Appointment of Group Senior Sustainability Officer (GSSO) to lead the Group’s sustainability initiatives.
Integration of Sustainability Risk Management across the 3LoD:
- Dedicated teams within CIB and Retail Banking units for overseeing sustainability and sustainable financing activities.
- Automated process established to assess and classify sustainable financing opportunities.
- Group Sustainability Unit – Responsible for managing and coordinating sustainability strategy related issues, developing action plans for the Group’s Net Zero portfolio strategies, as well as monitoring sustainability performance and coordinating sustainability-linked activities that enhance the Group’s impact. In this context, the Unit is responsible for facilitating the development of the Sustainability data framework to coordinate and prepare external and internal sustainability-related reports.
- Group Sustainability Risk – Overall responsible for overseeing, monitoring and managing sustainability risks.
- Intensive training on sustainability, sustainable finance and sustainability risk topics to Group personnel.
| Supervisory, Management & Administrative Bodies and Committees | Description of Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Eurobank Holdings / Eurobank Board of Directors (BoDs/Boards) | Provides entrepreneurial leadership, establishes strategic objectives, ensures resource availability and evaluates management performance. As per international best practices, the Boards oversee the Group’s Sustainability Strategy through the regular inclusion of sustainability items in the agendas of Board Meetings. |
| Eurobank Holdings / Eurobank Board Risk Committee (BRC) | Advises and supports the Board of Directors (BoD) in monitoring the Group's risk appetite and strategy, ensuring alignment with the business strategy and values. It oversees the implementation of risk strategies, including capital, liquidity, credit, market, sustainability and non-financial risks. The BRC consists of 5 non-executive directors, meets at least 10 times a year, and reports to the BoD quarterly and as needed. |
| Eurobank Management Risk Committee (MRC) |
Oversees the risk management framework, ensures material risks – including climate and environmental risks – are identified and escalated to the Board Risk Committee (BRC), and ensures necessary policies and procedures are in place to manage risks and comply with regulatory requirements. |
| Eurobank Sustainability Management Committee (Sustainability ManCo-SMC) |
Provides strategic direction on sustainability initiatives, reviews the Sustainability Strategy, Net Zero targets and transition plans prior to approval, ensures that the elements of the Sustainability Strategy and the Net Zero commitments are integrated into the Group’s business model and operations, approves changes in eligible assets of Green Bond and Sustainable Finance Frameworks, regularly measures and analyses the progress of the Sustainability Strategy goals and performance targets and ensures the proper implementation of sustainability-related policies and procedures, in accordance with supervisory requirements and voluntary commitments. |
| Eurobank Climate Risk Stress Test Committee (CRSTC) |
Designs and executes the Group’s CRST Programme, coordinates all related activities including risk identification, scenario design, and stress test execution, and reviews and challenges the output before escalating it to the Executive Board. |
| Group Senior Sustainability Officer (GSSO) |
Leads and coordinates the Group’s sustainability initiatives, oversees the sustainability programs of international subsidiaries, fosters a culture of sustainability, collaborates with senior management to embed sustainability into the Group’s strategic decision-making processes, secures and allocates resources, advocates for investments, and serves as the liaison with market/external stakeholders to ensure the Group remains at the forefront of sustainability innovation and compliance. |
| Group Sustainability Unit |
Manages and coordinates sustainability strategy related issues, and the development of action plans for the Group’s Net Zero portfolio strategies, as well as monitors sustainability performance and coordinates sustainability-linked activities that enhance the Group’s impact. In this context, the Unit facilitates the development of the Sustainability data framework to coordinate and prepare external and internal sustainability-related reports. |
| Business Units (Corporate and Investment Banking and Retail Banking) |
Execute portfolio-related sustainable activities, including the implementation of the FIS, with key responsibilities in sustainability strategy, sustainable financing/funding and investments, and sustainability risk management. |
| Group Sustainability Risk |
Monitors and manages sustainability risks, prepares and maintains sustainability risk management policies, leads the development and implementation of sustainability risk-related frameworks, monitors the Climate Risk action plan, reviews and challenges the Financed Impact Strategy, leads the sustainable lending re-assessment process, develops and coordinates Climate Risk Stress Testing and sustainability risk scenario analysis at Group level. |
| Group Compliance |
Monitors regulatory changes and alignment, designs compliance risk assessment methodologies, maintains conduct-related policies, and oversees sustainability product offerings to ensure they meet regulatory standards and do not misrepresent the Bank's products or services. |
| Group Internal Audit (Group IA) |
Independently reviews the adequacy and effectiveness of the internal control framework in place regarding Sustainability risk management, following a risk-based approach in line with its Annual Risk Assessment and Audit Planning Methodology, ensuring comprehensive coverage through risk assessments, professional upskilling, and dedicated audit planning. |
Alignment of the Remuneration Policy with the Group’s sustainability risks objectives:
Promotes sound and effective risk management, aligns with the Group's business and risk strategy and sustainability risk factors, avoids conflicts of interest and excessive risk-taking, and ensures gender neutrality, internal equity, and link to long-term performance.
Operating model
Integration of Sustainability Risk Management across the 3LoD
Eurobank integrates sustainability risk management across 3LoD:
- The 1st line involves the Business Units (CIB and Retail Banking), which are responsible for assessing, managing and monitoring risk levels in all risk categories, including sustainability risks. The CIB Sustainability Centre of Excellence and the Retail Banking sustainability coordinators are responsible for undertaking all relevant sustainability and sustainable finance activities. In addition, the role of the Group Sustainability Unit in the 1st line includes the responsibility for managing and coordinating sustainability strategy related issues, developing action plans for the Group's Net Zero portfolio strategies, and facilitating the Sustainability data framework development, as well as Sustainability Reporting, Environmental & Energy Reporting (EMAS Report, Greenhouse Gases Emissions Report per ISO14064) and Sustainability ratings. The 1st line, in coordination with other Units, executes and monitors financed, and specific operational sustainable goals and performance targets based on the Group’s Sustainability Strategy and in line with the Net Zero Strategy.
- The 2nd line is Group Risk Management (GRM), which sets the risk strategy and oversees sustainability risks through the dedicated Group Sustainability Risk.
- The 3rd line is the Group Internal Audit (Group IA), which independently reviews the adequacy and effectiveness of the internal control framework for sustainability risk management.
Sustainable Finance Framework assessment tool
The Group developed a web-based Sustainable Finance Framework (SFF) assessment tool for the Corporate and Investment Banking (CIB) portfolio, so as to underpin the classification and evaluation of sustainable/green financing opportunities in a structural manner, as part of the loan origination process. The SFF assessment tool is integrated into Drive+, which automates the process of assessing the Bank’s financing solutions against the criteria defined in the SFF.
ESG awareness and capacity building
Eurobank prioritises the development of its employees’ capabilities to ensure that they effectively assist clients in their sustainability efforts and facilitate their green transition. To this end, Eurobank implemented an ESG upskilling plan that includes internal awareness sessions and dedicated training programmes.
Employee ESG awareness training modules
The "ESG Thinking" awareness programme, launched in 2022, consists of 3 modules:
- ESG and the World
- ESG and the Bank
- ESG and Me
Since its launch, 4,788 employees have participated in the "ESG Thinking" programme, totalling 9,834 learning hours.
Stakeholder engagement and double materiality assessment
Eurobank fosters two-way communication and maintains an ongoing dialogue with stakeholders to address their expectations and concerns, while adopting a forward-looking approach by integrating the concept of Double Materiality Assessment into its operational and financed activities.Stakeholder engagement
An integral part of the Group’s approach to sustainability is to foster strong relationships of trust, cooperation and mutual benefit with all stakeholders affected by its activities, directly or indirectly. In this context, the Group promotes two-way communication and develops ongoing dialogue with stakeholders, to be able to actively meet the expectations, concerns and issues raised by all its stakeholders.
Stakeholders groups:
- Board of Directors
- Executive Management
- Investors, Shareholders and Investment Community
- Employees
- Business Community (including corporate networks, entrepreneurship, industry associations, financial institutions and startup entrepreneurs)
- Civil Society (including communities, NGOs, the academic and scientific community, international organisations and the Media)
- Customers and Clients
- Government and Regulators
- Suppliers and Partners
Double Materiality assessment
The Group’s double materiality assessment is the process that largely shapes the content of the Annual Report 2024 – Business & Sustainability. Following the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS), the Group evaluated sustainability impacts from its activities, and assessed risks and opportunities with financial influence across its value chain. The Double Materiality Assessment is conducted on an annual basis.
The methodology was carried out in 4 phases:
- Understanding of the business, value chain and related activities
Catergorising the Group's activities and partners within the value chain as upstream, downstream or within own operations, and mapping significant activities to relevant ESRS Sectors using methodologies such as the SASB Materiality Map and the MSCI ESG Industry Materiality Map. - Stakeholder engagement and identification of IROs
Conducting comprehensive consultations with affected stakeholders to collect diverse perspectives on impacts, risks and opportunities (IROs). Stakeholders were categorised into primary/affected, secondary and ESG experts, and these insights were used to update both the impact and financial materiality. This process involved mapping key stakeholders and analysing ESRS topics with sources such as sustainability ratings, industry reports and benchmarking analyses, identifying impacts, risks and opportunities. - Assessment of IROs
Conducting both impact and financial materiality assessments by scoring identified impacts, risks and opportunities on predefined scales for severity and likelihood. Performing impact materiality assessment through sustainability questionnaires, involving both internal and external stakeholders who evaluated impacts using a predefined assessment scale. Similarly, in the context of financial materiality, risks and opportunities were assessed through focus groups with key internal stakeholders participating. - Material topics
Analysing the collected data to prioritise IROs using scores from structured questionnaires (impact materiality assessment) and focus groups (financial materiality assessment), classifying topics as material based on impact and/or financial perspectives, and mapping material IROs to relevant topics for reporting. The double materiality assessment was reviewed and approved by the Sustainability Management Committee, in accordance with ESRS standards.
The Group plays a central role in the financial services value chain by linking a diverse range of upstream suppliers with downstream clients. The following graph illustrates the key sectors involved in its value chain:
For further information on the materiality analysis, refer to the Sustainability Statement.
For further information on stakeholder engagement as well as the means of communication and response, refer to the Sustainability Statement.
Material topics
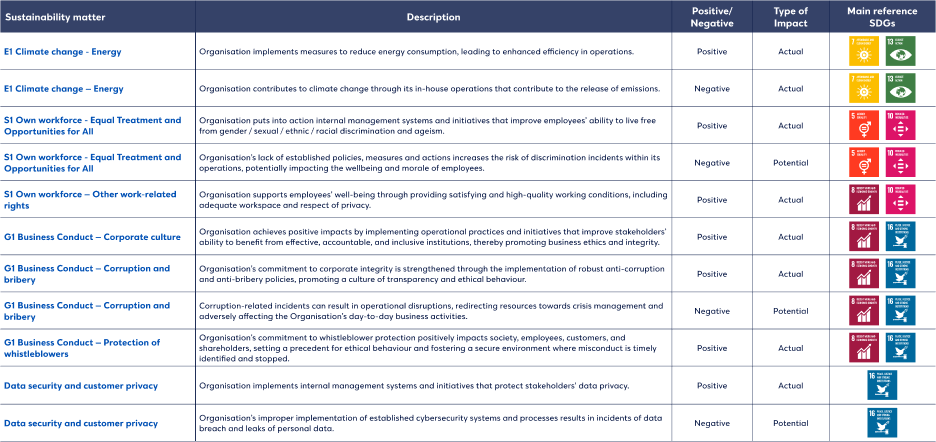
Topics can be identified as material from either an impact or a financial materiality perspective. A detailed analysis of material impacts, risks and opportunities resulting in material sustainability matters is available below.
Impact materiality
The table below outlines the outcomes of the Group's impact materiality assessment, presenting the identified material impacts:

Financial materiality
The table below outlines the outcomes of the Group's financial materiality assessment, presenting the identified material risks and opportunities:

Double materiality matrix
Sustainability ratings
Eurobank actively participates in internationally renowned sustainability ratings to showcase its continuous improvement in environmental, social and governance (ESG) performance, enhance disclosures, and boost investor confidence.Read more
In 2024, Eurobank achieved significant advancements in key sustainability ratings, including Sustainalytics and S&P. Notably, Sustainalytics ranked Eurobank in the highest risk category – "Negligible” – making it the first Greek bank to receive this top rating. Achieving the important ESG Regional Top Rated 2025 and ESG Industry Top Rated 2025 distinctions, Eurobank is placed among the top 4% of banks worldwide (30th out of 1,015 banks).
| Sustainability ratings and indices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sustainability Ratings and Indices | FY20241 | FY2023 |
| SUSTAINALYTICS | 9.7 / Negligible ▲ |
10.6 / Low Risk ▲ |
| MSCI* | Α |
Α ▲ |
| S&P GLOBAL | 56 ▲ | 52 ▲ |
| Other Sustainability ratings | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sustainability ratings and indices | FY2024 |
FY2023 |
| CDP | B | B ▲ |
| ATHEX ESG INDEX | ✓ | ✓ |
| REFINITIV | 85▲ | 79 |
| FTSE4GOOD | ✓ | ✓ |
| ISS ESG | E:1 / S:2 / G:4 | E:1 / S:2 / G:3 |
▲ improvement
1Sustainability Ratings scores regarding year of reference.
*In July 2024, Moody’s Analytics partnered with MSCI, leading to the discontinuation of Moody’s ESG Assessments. The last assessment pertained to FY2023.












